Liquidity Mining: What Is It and How Does It Work in DeFi?

Liquidity mining is a DeFi process where you earn rewards by adding your crypto tokens to a liquidity pool. It works through smart contracts, letting traders swap tokens while you earn a share of the fees and sometimes bonus tokens.
The benefits of liquidity mining are earning passive income without having to trade actively. It also allows your idle tokens to work for you by collecting trading fees. You can even help DeFi platforms stay functional by supplying much-needed liquidity. In return, you often receive bonus tokens, which may increase in value.
This guide will cover what DeFi liquidity mining is, its pros and cons, and how it works. We will also explain how to start liquidity mining and whether it is a safe and legitimate process.
What Is Liquidity Mining in DeFi?
Liquidity mining is a way to earn rewards by adding your crypto to DeFi liquidity pools. Generally, you have to lock your tokens in a pool, and in return, you will get rewards like extra tokens or part of trading fees. The best platforms for most of the liquidity miners are Uniswap, PancakeSwap, or Curve.
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) require these pools of assets, known as liquidity, to enable trading for their users. Generally, these platforms operate on smart contracts without a central authority. For example, you might put some Ethereum and some of another token into a pool, mostly USDT or USDC. Then, when other people trade these tokens, you get a small part of the trading fee.
In simple words, DeFi platforms need liquidity from you to run smoothly. So, they give rewards to users who provide it. It is always a win-win deal, as you help the system work, and you get paid for it in return.
How Does Liquidity Mining Work?
Liquidity mining works based on an architecture that includes Automated Market Makers (AMMs) and smart contracts. An individual, as a Liquidity Provider (LP), initially chooses a liquidity pool on a DEX. The person then has to deposit an asset pair (ETH/USDC) into the respective contract of the pool, often in equal monetary amounts.
As payment for this deposit, the smart contract of the Ethereum protocol automatically mints and transfers LP tokens to the user. These tokens constitute a tokenized form of that user’s particular proportion of the overall assets in that pool.
Liquidity mining rewards come in two stages. The first is that the LP receives a portion of the trading fees incurred in that pool whenever a trader conducts a swap. Second, for the real “mining,” the LP typically stakes its accrued LP tokens into a different contract, which is referred to in some cases as a master contract. This staking action qualifies them to earn additional rewards. These are mainly paid out in the platform’s governance token. The amount of these mined tokens is usually proportional to the number of LP tokens staked and the duration of the staking period.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Liquidity Mining?
Pros of Liquidity Mining
The pros of liquidity mining are passive income, high returns, low entry barrier, decentralization support, and enhanced token utility.
- Passive Income Opportunity: One of the greatest attractions is the potential to earn passive income. You just put your crypto assets into a liquidity pool, and as long as they’re there, you’ll get a portion of the transaction fees that the platform generates. Your crypto is generating income for you without you actually having to do anything yourself.
- High Returns: Liquidity mining occasionally has really high annual percentage rates (APRs), which are sometimes way above what you’d find in conventional finance.
- Low Entry Barrier: You don’t have to be a large investor to become a part of it. Most of the platforms enable you to provide smaller portions of crypto, and that makes it accessible for a wider range of people who want to explore a decentralized trading environment.
- Supports Decentralization: With liquidity mining, you’re essentially helping exchanges and other DeFi protocols in their operations. This enables these platforms to work well without the need for central intermediaries, which is a fundamental concept of decentralized finance.
- Increased Token Utility: When tokens are locked up in liquidity pools, they’re actively used to facilitate trading. This increased utility can, in turn, enhance the investment portfolio value and overall ecosystem of the tokens you’re holding.
Cons of Liquidity Mining
The cons of liquidity mining are impermanent loss, smart contract risks, learning complexity, and rug pulls.
- Impermanent Loss: This is likely the biggest risk involved. Impermanent loss occurs when the value of the tokens you added to a liquidity pool drops substantially from when you originally added them. If a token within a pair decreases significantly relative to the other, you may receive less than you would have if you had simply kept your tokens out of the pool.
- Smart Contract Vulnerability: DeFi platforms depend a lot on smart contracts, which are basically self-executing contracts. If something goes wrong or is buggy with these contracts, then hackers might end up exploiting them, meaning you could lose your deposited money. It is a technical risk that always exists in this segment.
- Complexity and Learning Curve: For newcomers, understanding how liquidity mining works, including concepts like impermanent loss, pool composition, and reward mechanisms, can be quite overwhelming. It’s not always a straightforward process, and it requires a bit of research and understanding to do it safely.
- Rug Pulls and Scams: There’s always the risk of bad projects in the crypto universe. Some projects can be designed as “rug pulls,” where the dev team withdraws all the liquidity from the pool without any notification, leaving investors with valueless tokens. It’s important to research a project quite extensively before joining.
What Are the Risks Associated With Liquidity Mining?
Risks of liquidity mining are mostly related to price changes, smart contract bugs, and project security. One major risk is impermanent loss, where token values shift and you end up with less than you started. Even if the pool seems stable, sudden market moves can hurt your returns depending on your risk tolerance. Another risk comes from poorly written contract codes that hackers can exploit, which has happened before.
Liquidity mining scams are also common, where fake projects promise high rewards and then disappear with the funds. Of course, the crypto market is generally volatile, so rewards can change quickly. Basically, without proper research, you could lose money.
What Strategies Can Help Reduce Risk in Liquidity Mining?
First, do your research on the project. Before you invest in any liquidity pool, thoroughly investigate the project’s whitepaper, its team, and its community. You have to search for established protocols that have a solid reputation. This will help you steer clear of those horrible “rug pulls” and other liquidity mining scams.
The second main tactic is selecting stablecoin pairs. If you supply liquidity using stablecoins (such as USDT, USDC, or DAI), you automatically minimize your exposure to impermanent loss. Also, diversification is your friend, as with any investment. Don’t invest all your crypto in one liquidity pool or even on one exchange.
Always look for platforms that have had their code thoroughly audited by reputable third parties. Of course, this doesn’t completely eliminate the risk of exploits, but it significantly reduces it.
What Are Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) and Automated Market Makers (AMMs)?
Decentralized exchanges, or DEXs, are platforms where you can trade crypto directly from your wallet. There’s no middleman, no account setup, and no bank needed. Also, these DEXs don’t use order books like traditional markets. Instead, they use something called Automated Market Makers (AMMs).
Now, an Automated Market Maker (AMM) is a type of DEX, but it works a little differently. Instead of relying on an order book where buyers and sellers list their desired prices, AMMs use a special mathematical formula to set the prices of assets. These formulas operate on liquidity pools. So, instead of trading with another person, you’re essentially trading directly with this pool of assets.
How Do DEXs and AMMs Enable Liquidity Mining?
DEXs, especially those powered by AMMs, need a constant supply of cryptocurrency in their pools to facilitate all those trades. If there isn’t enough crypto in the pools, trades become difficult, and prices fluctuate.
These pools need liquidity provision to function, and that’s where liquidity mining comes in. When you add digital assets to a pool, you help the system run, and in return, you earn rewards. Generally, these rewards come from trading fees and bonus tokens. AMMs handle all trades from these pools, so every trade gives a small fee to the people who added tokens.
What Is a Liquidity Mining Pool and How Does It Work?
A liquidity mining pool is a smart contract that holds two tokens, like ETH and USDC. You deposit an equal value of both tokens into the pool. The pool then allows traders to swap between them.
Here’s how it works: When someone wants to trade, say, ETH for USDC, they don’t buy it from another individual. Instead, they interact with this pool. The AMM’s formula determines the exchange rate based on the current ratio of ETH to USDC in the pool. When a trade happens, a small fee is usually charged, and this fee is then distributed proportionally among all the liquidity providers based on how much they’ve contributed to the pool. So, the more liquidity you provide, the larger your share of the rewards.
How to Start Liquidity Mining?
To start liquidity mining, you need to choose a crypto wallet and deposit your funds into it. Then, connect the wallet to a DeFi protocol like Uniswap. After that, select a token pair and provide liquidity to the protocol.
Step 1: Get a Compatible Wallet and Some Crypto
First thing you’ll need is a non-custodial crypto wallet that can connect to your chosen decentralized applications (dApps). Now, make sure you have some cryptocurrency in it. To start liquidity mining on Uniswap, you’ll typically need two different tokens of equal dollar value for the liquidity pool. So, if you want to add to an ETH/USDC pool, you’d need, say, $100 worth of ETH and another $100 worth of USDC. You can buy tokens from popular centralized exchanges like Binance. If you want to know more, here is our in-depth Binance review.
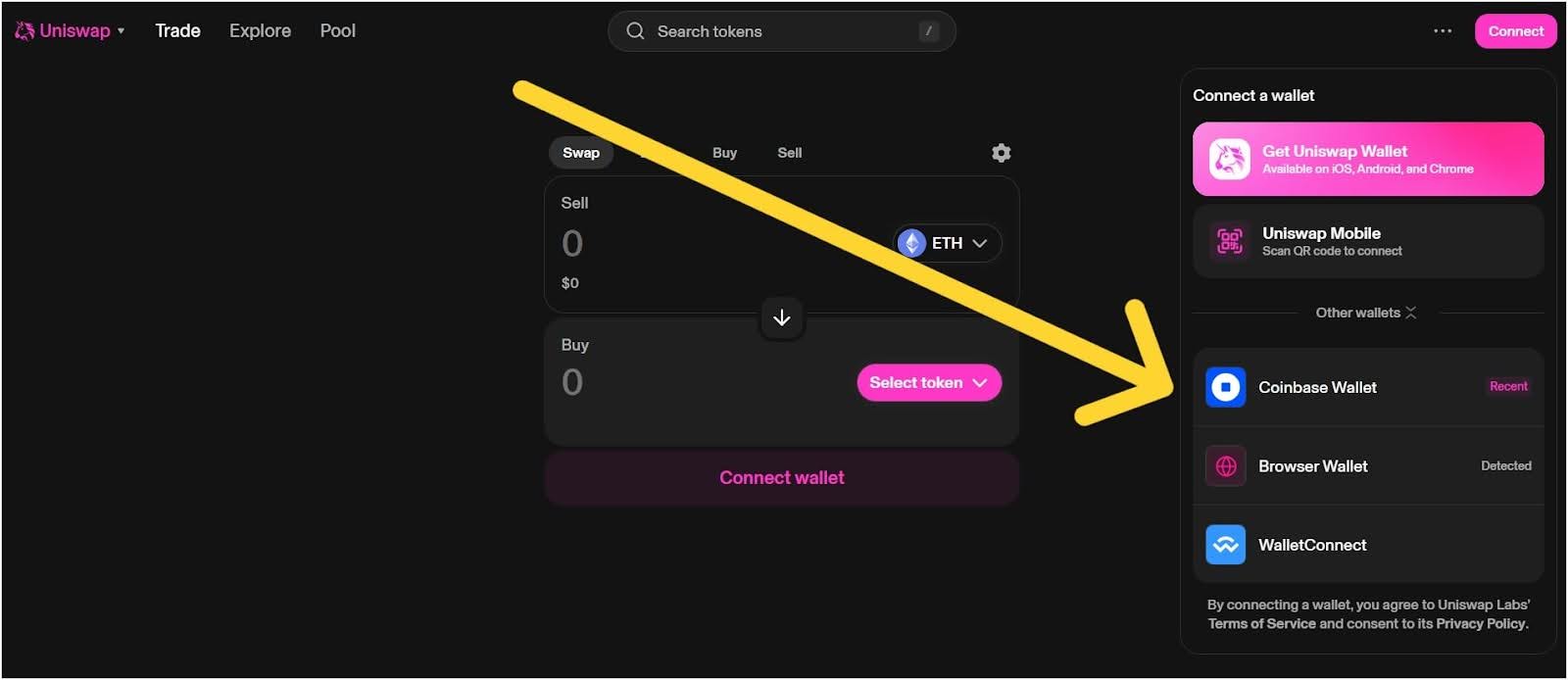
Step 2: Head to the DEX and Connect Your Wallet
Go to the Uniswap website (app.uniswap.org). On the site, you’ll see a “Connect Wallet” button, which is usually in the top right corner. Click that and follow the prompts to connect your MetaMask or other compatible wallet. It will link your wallet to the Uniswap platform.
Step 3: Choose Your Liquidity Pool
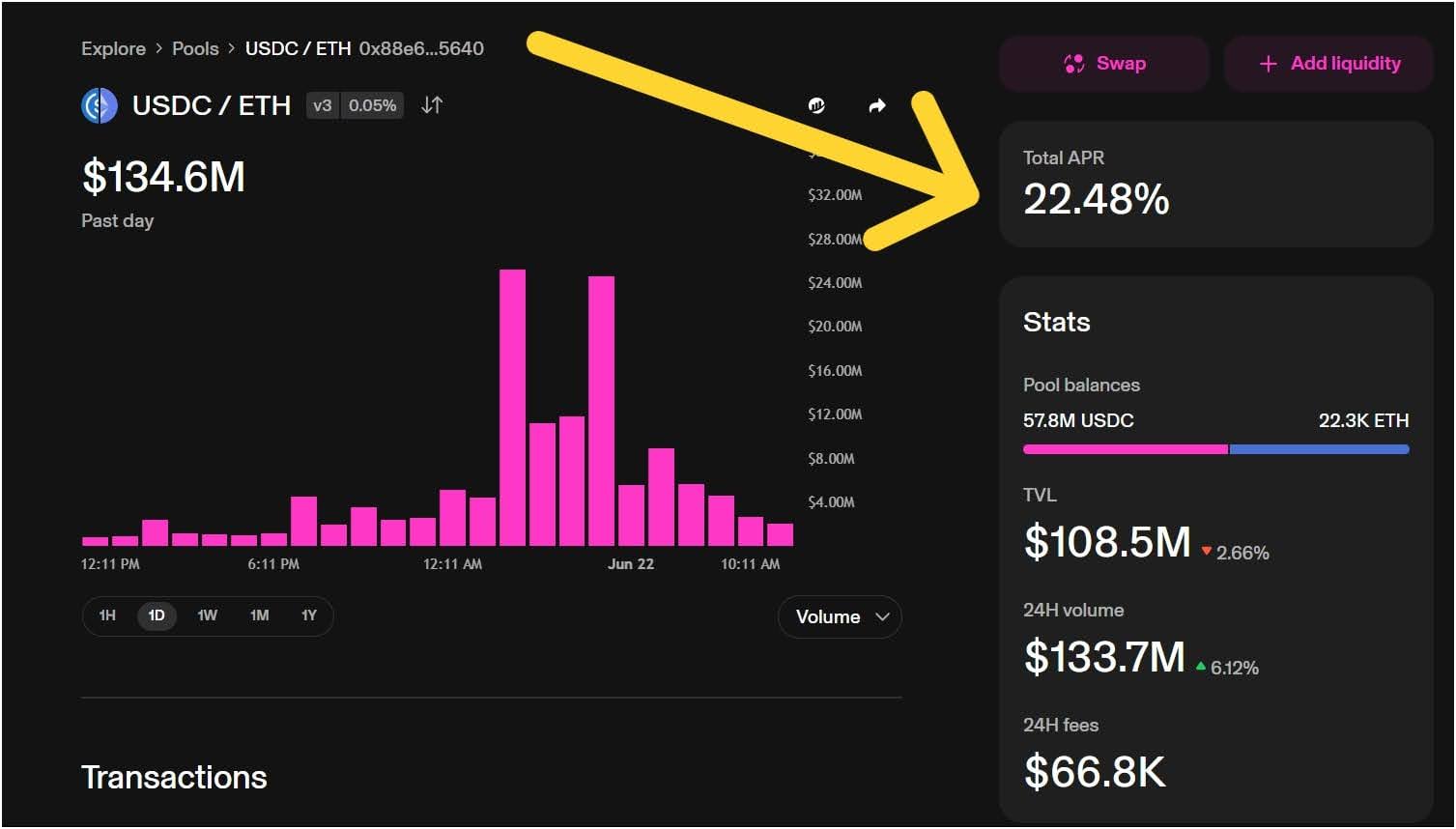
Once you have connected your wallet, you need to navigate to the “Pool” section. You’ll then need to select which pair of tokens you want to provide liquidity for. Uniswap offers various pools, and you’ll typically pick one that you’re comfortable holding both tokens for. Remember, you’ll need to provide an equal value for each token.
On Uniswap v3, you also get to choose a fee tier and a price range; this lets you concentrate your liquidity, which can earn more fees but also is very risky as it increases impermanent loss risk if prices move out of your chosen range.
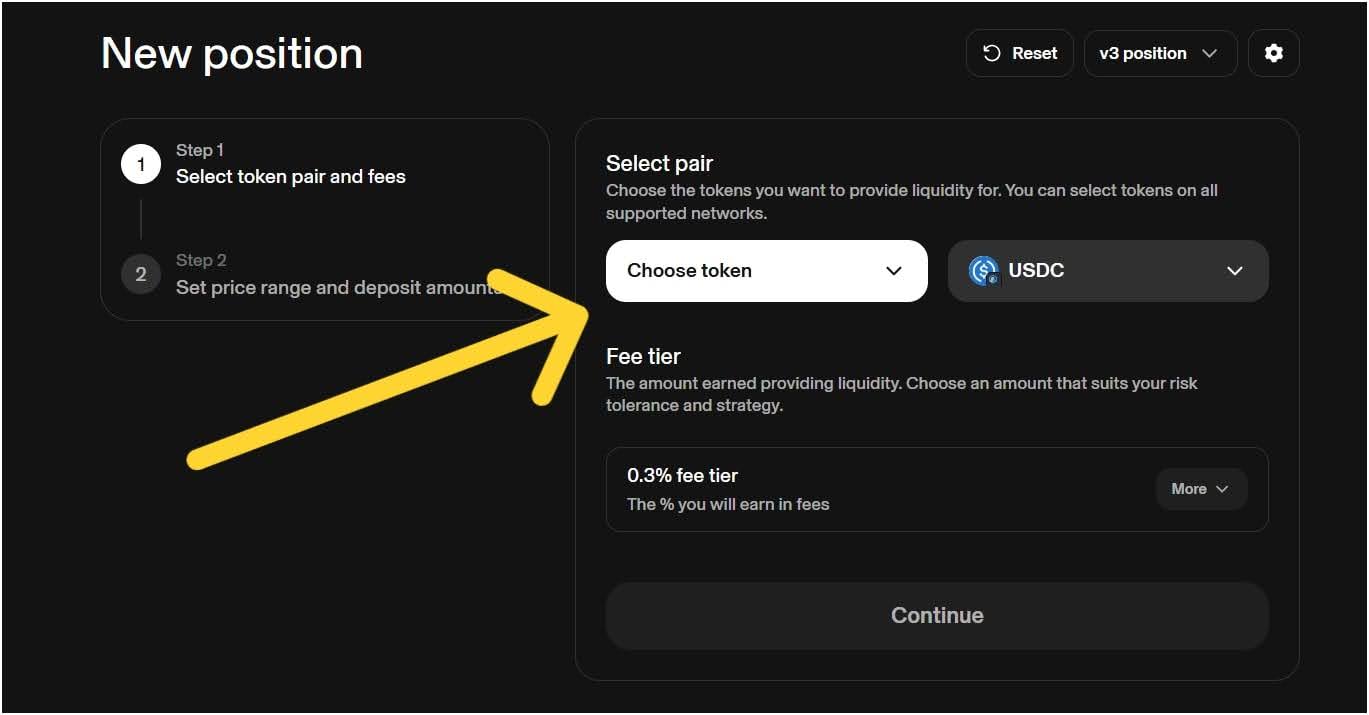
Step 4: Deposit Your Tokens and Get LP Tokens
You’ll need to enter the amount of tokens you want to deposit. The platform will automatically calculate the corresponding amount of the other token needed. Now, confirm the transaction in your wallet, and your tokens will be added to the liquidity pool.
In return, you’ll receive “LP tokens” (Liquidity Provider tokens), which you can call a receipt representing your share of that pool. These LP tokens are what you hold to prove your contribution and to later claim your share of the fees and rewards.
How Do Liquidity Providers Contribute to Liquidity Mining?
Liquidity providers contribute to mining by joining a pool and then depositing two tokens of equal value, like ETH and USDC. These tokens help traders swap between pairs on decentralized platforms. In return, the provider earns rewards, usually from trading fees and sometimes bonus tokens. The more they add, the more they earn. Basically, without these providers, the platform won’t have enough liquidity for smooth trades. You can also explore our guide on exit liquidity to learn more about the crypto liquidity part.
Is Liquidity Mining Profitable?
Yes, liquidity mining can be profitable, but there are many associated risks. The profitability depends on things like the trading volume in the pool, the specific reward tokens offered, and crucially, how well the prices of the deposited assets hold up. High trading volumes mean more fees distributed, and if the incentive tokens gain value, that’s a bonus. But risk exposure, like impermanent loss and market volatility, can affect profits. So yes, it can work, but it’s not guaranteed income.
Is Liquidity Mining the Same as Yield Farming?
No, they’re not quite the same, though they are very closely related. Liquidity mining focuses purely on providing liquidity to a decentralized exchange’s pools and earning rewards for doing so.
Now, yield farming is a much wider strategy that involves moving crypto assets across various DeFi protocols to find the best possible returns, which can include lending, borrowing, and staking, in addition to liquidity mining. So, liquidity mining is a part of yield farming.
Is Liquidity Mining Legit?
Yes, liquidity mining is legit when done on trusted DeFi platforms like Uniswap, Curve, or Aave. It works through smart contracts and rewards users who help the system with liquidity. But scams do exist, especially from fake or unverified projects.
The post Liquidity Mining: What Is It and How Does It Work in DeFi? appeared first on CryptoNinjas.